TensorBoard: Visualizing Learning
The computations you'll use TensorFlow for - like training a massive deep neural network - can be complex and confusing. To make it easier to understand, debug, and optimize TensorFlow programs, we've included a suite of visualization tools called TensorBoard. You can use TensorBoard to visualize your TensorFlow graph, plot quantitative metrics about the execution of your graph, and show additional data like images that pass through it. When TensorBoard is fully configured, it looks like this:
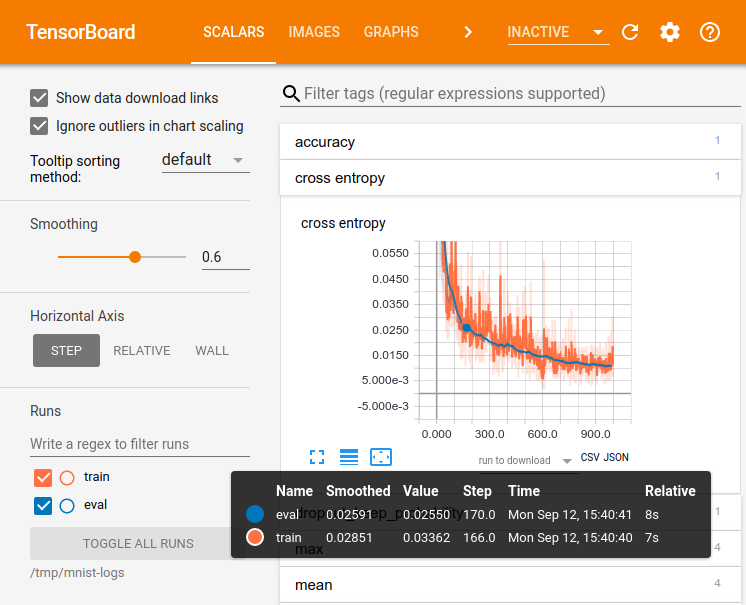
This tutorial is intended to get you started with simple TensorBoard usage. There are other resources available as well! The TensorBoard README has a lot more information on TensorBoard usage, including tips & tricks, and debugging information.
Serializing the data
TensorBoard operates by reading TensorFlow events files, which contain summary data that you can generate when running TensorFlow. Here's the general lifecycle for summary data within TensorBoard.
First, create the TensorFlow graph that you'd like to collect summary data from, and decide which nodes you would like to annotate with summary operations.
For example, suppose you are training a convolutional neural network for
recognizing MNIST digits. You'd like to record how the learning rate
varies over time, and how the objective function is changing. Collect these by
attaching tf.summary.scalar ops
to the nodes that output the learning rate and loss respectively. Then, give
each scalar_summary a meaningful tag, like 'learning rate' or 'loss
function'.
Perhaps you'd also like to visualize the distributions of activations coming
off a particular layer, or the distribution of gradients or weights. Collect
this data by attaching
tf.summary.histogram ops to
the gradient outputs and to the variable that holds your weights, respectively.
For details on all of the summary operations available, check out the docs on summary operations.
Operations in TensorFlow don't do anything until you run them, or an op that
depends on their output. And the summary nodes that we've just created are
peripheral to your graph: none of the ops you are currently running depend on
them. So, to generate summaries, we need to run all of these summary nodes.
Managing them by hand would be tedious, so use
tf.summary.merge_all
to combine them into a single op that generates all the summary data.
Then, you can just run the merged summary op, which will generate a serialized
Summary protobuf object with all of your summary data at a given step.
Finally, to write this summary data to disk, pass the summary protobuf to a
tf.summary.FileWriter.
The FileWriter takes a logdir in its constructor - this logdir is quite
important, it's the directory where all of the events will be written out.
Also, the FileWriter can optionally take a Graph in its constructor.
If it receives a Graph object, then TensorBoard will visualize your graph
along with tensor shape information. This will give you a much better sense of
what flows through the graph: see
Tensor shape information.
Now that you've modified your graph and have a FileWriter, you're ready to
start running your network! If you want, you could run the merged summary op
every single step, and record a ton of training data. That's likely to be more
data than you need, though. Instead, consider running the merged summary op
every n steps.
The code example below is a modification of the
simple MNIST tutorial,
in which we have added some summary ops, and run them every ten steps. If you
run this and then launch tensorboard --logdir=/tmp/tensorflow/mnist, you'll be able
to visualize statistics, such as how the weights or accuracy varied during
training. The code below is an excerpt; full source is
here.
def variable_summaries(var):
"""Attach a lot of summaries to a Tensor (for TensorBoard visualization)."""
with tf.name_scope('summaries'):
mean = tf.reduce_mean(var)
tf.summary.scalar('mean', mean)
with tf.name_scope('stddev'):
stddev = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(var - mean)))
tf.summary.scalar('stddev', stddev)
tf.summary.scalar('max', tf.reduce_max(var))
tf.summary.scalar('min', tf.reduce_min(var))
tf.summary.histogram('histogram', var)
def nn_layer(input_tensor, input_dim, output_dim, layer_name, act=tf.nn.relu):
"""Reusable code for making a simple neural net layer.
It does a matrix multiply, bias add, and then uses relu to nonlinearize.
It also sets up name scoping so that the resultant graph is easy to read,
and adds a number of summary ops.
"""
# Adding a name scope ensures logical grouping of the layers in the graph.
with tf.name_scope(layer_name):
# This Variable will hold the state of the weights for the layer
with tf.name_scope('weights'):
weights = weight_variable([input_dim, output_dim])
variable_summaries(weights)
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
biases = bias_variable([output_dim])
variable_summaries(biases)
with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'):
preactivate = tf.matmul(input_tensor, weights) + biases
tf.summary.histogram('pre_activations', preactivate)
activations = act(preactivate, name='activation')
tf.summary.histogram('activations', activations)
return activations
hidden1 = nn_layer(x, 784, 500, 'layer1')
with tf.name_scope('dropout'):
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
tf.summary.scalar('dropout_keep_probability', keep_prob)
dropped = tf.nn.dropout(hidden1, keep_prob)
# Do not apply softmax activation yet, see below.
y = nn_layer(dropped, 500, 10, 'layer2', act=tf.identity)
with tf.name_scope('cross_entropy'):
# The raw formulation of cross-entropy,
#
# tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(tf.softmax(y)),
# reduction_indices=[1]))
#
# can be numerically unstable.
#
# So here we use tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits on the
# raw outputs of the nn_layer above, and then average across
# the batch.
diff = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(targets=y_, logits=y)
with tf.name_scope('total'):
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(diff)
tf.summary.scalar('cross_entropy', cross_entropy)
with tf.name_scope('train'):
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(FLAGS.learning_rate).minimize(
cross_entropy)
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
with tf.name_scope('correct_prediction'):
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1))
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
tf.summary.scalar('accuracy', accuracy)
# Merge all the summaries and write them out to /tmp/mnist_logs (by default)
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
train_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(FLAGS.summaries_dir + '/train',
sess.graph)
test_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(FLAGS.summaries_dir + '/test')
tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
After we've initialized the FileWriters, we have to add summaries to the
FileWriters as we train and test the model.
# Train the model, and also write summaries.
# Every 10th step, measure test-set accuracy, and write test summaries
# All other steps, run train_step on training data, & add training summaries
def feed_dict(train):
"""Make a TensorFlow feed_dict: maps data onto Tensor placeholders."""
if train or FLAGS.fake_data:
xs, ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100, fake_data=FLAGS.fake_data)
k = FLAGS.dropout
else:
xs, ys = mnist.test.images, mnist.test.labels
k = 1.0
return {x: xs, y_: ys, keep_prob: k}
for i in range(FLAGS.max_steps):
if i % 10 == 0: # Record summaries and test-set accuracy
summary, acc = sess.run([merged, accuracy], feed_dict=feed_dict(False))
test_writer.add_summary(summary, i)
print('Accuracy at step %s: %s' % (i, acc))
else: # Record train set summaries, and train
summary, _ = sess.run([merged, train_step], feed_dict=feed_dict(True))
train_writer.add_summary(summary, i)
You're now all set to visualize this data using TensorBoard.
Launching TensorBoard
To run TensorBoard, use the following command (alternatively python -m
tensorflow.tensorboard)
tensorboard --logdir=path/to/log-directory
where logdir points to the directory where the FileWriter serialized its
data. If this logdir directory contains subdirectories which contain
serialized data from separate runs, then TensorBoard will visualize the data
from all of those runs. Once TensorBoard is running, navigate your web browser
to localhost:6006 to view the TensorBoard.
When looking at TensorBoard, you will see the navigation tabs in the top right corner. Each tab represents a set of serialized data that can be visualized.
For in depth information on how to use the graph tab to visualize your graph, see TensorBoard: Graph Visualization.
For more usage information on TensorBoard in general, see the TensorBoard README.